An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solving some class of problem, or for performing some specific activity. Much like a recipe, they give very explicit instructions that lead to a desired goal. Algorithms play a very central role in computer science and can be applied in so many areas-from software development and data analysis to artificial intelligence.
The Word Algorithm means “A set of finite rules or instructions to be followed in calculations or other problem-solving operations.”
“A procedure for solving a mathematical problem in a finite number of steps that frequently involves recursive operations.”
Therefor Algorithm refers to a sequence of finite steps to solve a particular problem.
Use of The Algorithms
Algorithms play a crucial role in various fields and have many applications. Some of the key are as where algorithms are used include. Algorithms are essential tools that power modern technology and streamline processes in various fields.
1. Computer Science:
Algorithms form the basis of computer programming and are used to solve problems ranging from simple sorting and searching to complex tasks such as artifical intelligence and machine learning.
2. Mathematics:
Algorithms are used to solve mathematical problems, such as finding the optimal solution to a system of linear equations or finding the shortest path in a graph.
3. Operations Research:
Algorithms are used to optimize and make decisions in fields such as transportation, logistics and resource allocation.
4. Artifical Intelligence:
Algorithms are the foundation of artifical intelligence and machine learning and are used to develop intelligent systems that can perform tasks such as image recognition, natural languages processing and decision-making.
5. Data Science:
Algorithms are used to analyze, process and extract insights from large amounts of data in fields such as marketing, finance and healthcare. processing and decision-making.
Algorithms Can be Simple and Complex depending on what you want to achive
It can be understand by taking the example of cooking a new recipe. To Cook a new recipe one reads the the instructions and steps and executes them one by one, in the given sequence.
Every time you use your phone, computer, laptop or calculator you are using algorithms.
What is the need for algorithms?
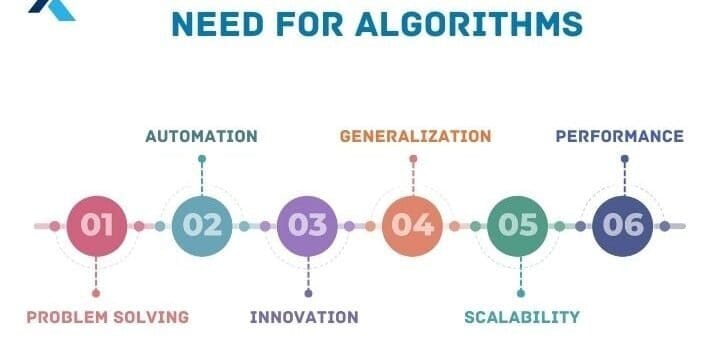
Algorithms are necessary for solving complex problems efficiently and effectively.
They help to automate processes and make them more reliable, faster and easier to perform.
Algorithms also enable computers to perform tasks that would be defficult or impossible for humans to do manually.
They are used in various fields such as mathematics, computer science, engineering, finance and many others to optimize processes, analyze data, make predictions and provide solutions to problems.
What are the characteristics of an algorithm?
As one would not follow any written instructions to cook the recipe, but only the standard one.
Clear and Unambiguous:– The algorithms should be unambiguous. Each of its steps should be clear in all aspects and must lead to only one meaning.
Well-Defined Inputs:– If an algorithm says to take inputs, it should be well-defined inputs. It may or may not take input.
Well-Defined Outputs:– The algorithm must elearly define what output will be yielded and it should be well-defined as well. It should produce at least 1(one) output.
Finite-ness:-The Algorithm must be finite, i.e. it should terminate after a finite time.
Feasible:– The algorithm must be simple, generic and practical, such that it can be executed with the available resources. It must not contain some future technology or anything.
Language Independent:– The algorithm designed must be language-independent, i.e. it must be just plain instructions that can be implemented in any language and yet the output will be the same as expected.
Input:– An algorithm has Zero or more inputs.
Output:– An algorithm produces at least one output.
Finiteness:– An algorithm must terminate after a finite number of steps in all test cases.
Definiteness:– All instructions in an algorithm must be unambiguous, precise and easy to interpret.
Effectiveness:– An algorithm must be developed by using very basic, simple and feasible operations so that one can trace it out by using just paper and pencil.
Properties of Algorithm
It should terminate after a finite time.
It should produce at least one output.
It should take zero or more input.
It should be deterministic means giving the same output for the same input case.
Every step in the algorithm must be effective i.e. every step should do some work.
Types of Algorithm
Brute Force Algorithm: The algorithm solves a problem by exhaustively searching through all possible solutions until the right one is obtained. It’s simple but, for large datasets, often inefficient.
Recursive Algorithm: A method by which a function calls itself to solve a problem by breaking down the problem into smaller subproblems. It’s useful for problems such as tree traversals but often results in using too much memory.
Backtracking Algorithm: The Backtracking Algorithm explores all possible solutions incrementally. It abandons paths to dead ends that represent invalid solutions. It is useful in solving constraint satisfaction problems like puzzles or combinatorial problems.
Searching Algorithm: The Searching Algorithm is algorithms that find particular elements of a collection (for example, binary search or linear search). Depending on the dataset size and its structure, efficiency varies.
Hashing Algorithm: It maps data to fixed-size values known as hash codes to speed up search operations. Hashing is often employed in data structures like hash tables for faster access.
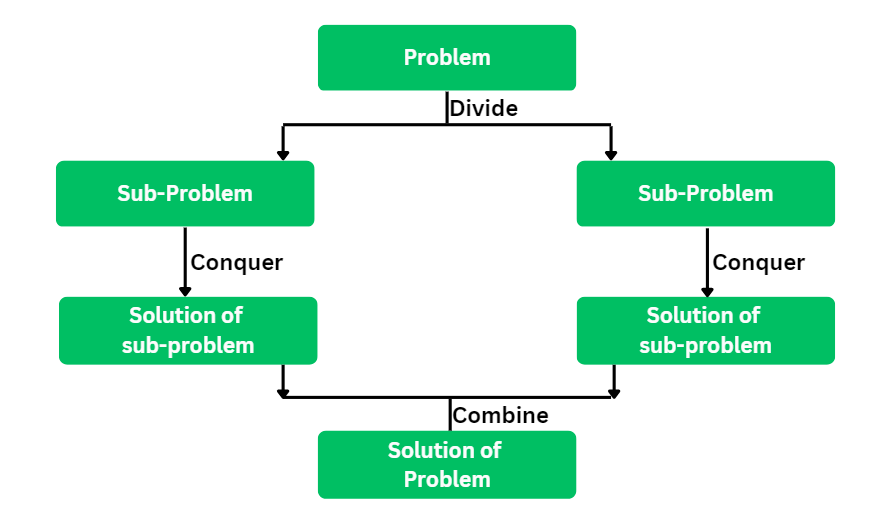
Divide and Conquer Algorithm: Divide the problem into pieces, apply the solutions to each instance separately, and combine those solutions of the subproblems to form the final result. Classical instances of the divide-and-conquer approach are Quick Sort and Merge Sort.
Greedy Algorithm: It has greedy algorithm as follows: Each stage does local optimum choices so that the outcome obtained is probably globally optimal. They are very applicable in optimization problems, for instance, such as coin change or scheduling.
Algorithm of Dynamic Programming: The problem is broken up into overlapping subproblems, and they are solved once, saving the results of subproblems from redundant computation.
Randomized Algorithm: These algorithms are based on logic employing randomness in their solution. They do not always give the same output but, on average, often solve complex problems better.
Backtracking Algorithm: This technique involves building candidate solutions incrementally and abandoning those that don’t comply with the constraints of the problem; more examples include Sudoku or the N-Queens puzzle.
Analyzing Algorithms
Analyzing/Analysis of algorithms is a fundamental aspect of computer science that involves evaluating performance of algorithms and programms. Efficiency is measured in terms of time and space.
Read Also
The post What is Algorithm | Introduction to Algorithms appeared first on TEKLOG.
